
创建自己的小题库
搜索
【单选题】


Caught in a squeeze between the health needs of ageing populations on one hand and the financial cr on the other, governments everywhere are looking for ways to slow the growth in healthcare spending. Increasingly ,they are looking to the generic-drugs(普通物) industry as a savior. In November Japan’s finance ministry issued a report complaining that the country’s use of generics was less than a third of that in America or Britain. In the stone month Canada’s competition watchdog criticized the country’s pharmacies for failing to pass on the savings made possible by the use of generic drugs. That greed, it reckoned, costs taxpayers nearly C $ 1 billion a year.
Then on November 28th the European Commission issued the preliminary results of its year-long probe into drug giants in the European Union. The report reached a ing, though provisional, conclusion: the drugs firms use a variety of unfair strategies to protect their expensive drugs by delaying the entry of cheaper generic opponents. Though this initial report does not carry the force of law (a final report is due early next year), it has caused much controversy. Neelie Kroes, the EU’s competition commissioner, says she is ready to take legal action if the evidence allows.
One strategy the investigators criticize is the use of the "patent cluster(专利群) ". A firm keen to defend its drug due to go off-patent may file dozens or hundreds of new patents, often of dubious merit, to confuse and terrify potential copycats and maintain its monopoly. An unnamed drugs firm once took out 1,300 patents across the EU on a single drug. The report also suggests that out-of-court settlements between makers of patented drugs and generics finals may be a strategy used by the former to delay market entry by the latter.
According to EU officials, such misdeeds have delayed the arrival of generic competition and the accompanying savings. On average, the report estimates, generics arrived seven months after a patented drug lost its protection, though where the drug was a big seller the lag was four months. The report says taxpayers paid about
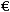 3 billion more than they would have had the generics gone on sale immediately.
3 billion more than they would have had the generics gone on sale immediately.
But hang on a minute. Though many of the charges of bad behavior leveled at the patented-drugs industry by EU investigators may well be true, the report seems to let the generics industry off the hook (钩子) too lightly. After all, if the drugs giants stand accused, in effect, of bribing opponents to delay the launch of cheap generics, shouldn’t the companies that accepted those "bribes" also share the blame
A.
What can we learn from the report issued by the European Commission

 分享
分享
 反馈
反馈 收藏
收藏 举报
举报参考答案:


举一反三
【多选题】Django1.11版本下,以下哪些方法是Django中间件提供的钩子方法()
A.
process_view
B.
process_exception
C.
process_template_response
D.
process_middleware_exception
【单选题】地线接地方式、地阻值应符合《传输接地规范》或满足设计文件要求,联合接地电阻:综合通信楼<()欧姆;普通机房<()欧姆(恶劣环境地区<()欧姆
A.
10、1、5
B.
1、10、5
C.
5、1、10
D.
1、5、10

相关题目:
【多选题】Django1.11版本下,以下哪些方法是Django中间件提供的钩子方法()
A.
process_view
B.
process_exception
C.
process_template_response
D.
process_middleware_exception
【单选题】地线接地方式、地阻值应符合《传输接地规范》或满足设计文件要求,联合接地电阻:综合通信楼<()欧姆;普通机房<()欧姆(恶劣环境地区<()欧姆
A.
10、1、5
B.
1、10、5
C.
5、1、10
D.
1、5、10

参考解析:


AI解析
重新生成

题目纠错 0
发布

 复制链接
复制链接 新浪微博
新浪微博 分享QQ
分享QQ 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫





