
创建自己的小题库
搜索
【单选题】


| Many theories concerning the causes of juvenile delinquency (crimes committed by young people) focus either on the individual or on society as the major contributing influence. Theories (31) on the individual suggest that children engage in criminal behavior (32) they were not sufficiently penalized for previous misdeeds or that they have learned criminal behavior through (33) with others. Theories focusing on the role of society suggest that children commit crimes in (34) to their failure to rise above their socioeconomic status, (35) as a rejection of middle-class values. Most theories of juvenile delinquency have focused on children from disadvantaged families, (36) the fact that children from wealthy homes also commit crimes. The latter may commit crimes (37) lack of adequate parental control. All theories, however, are tentative and are (38) to criticism. Changes in the social structure may indirectly (39) juvenile crime rates. For example, changes in the economy that (40) to fewer job opportunities for youth and rising unemployment (41) make gainful employment increasingly difficult to obtain. The resulting discontent may in (42) lead more youths into criminal behavior. Families have also (43) changes these years. More families consist of one-parent households or two working parents (44) , children are likely to have less supervision at home (45) was common in the traditional family (46) .This lack of parental supervision is thought to be an influence on juvenile crime rates. Other (47) causes of offensive acts include frustration or failure in school, the increased (48) of drags and alcohol, and the growing (49) of child abuse and child neglect. All these conditions tend to increase the probability of a child committing a criminal act, (50) a direct causal relationship has not yet been established. |
A.
on
B.
in
C.
for
D.
with

 分享
分享
 反馈
反馈 收藏
收藏 举报
举报参考答案:

举一反三
【单选题】2003年非粮食作物的种植总面积约为()。 A.62万公顷 B.156万公顷 C.138万公顷 D.103万公顷
A.
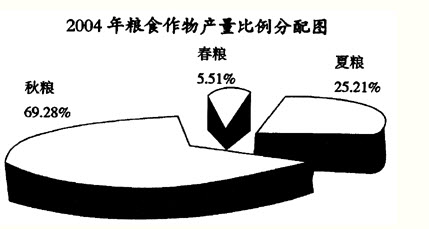
2004年某省种植业结构继续调整,粮食作物的种植面积占农作物种植总面积比例由上午的60.2%调整为58.4%,年粮食作物种植面积147.11万公顷,比去年减少9.0公顷,粮食总产量713.16万公顷,其中春、夏、秋粮所占比例如下图所示。与去年相比,春粮减产5.31万吨,夏粮减产2.37万吨,秋粮减产42.38万吨,总产量下降50.06万吨。非粮食作物中的油料、蔬菜、药材种植面积分别增长1.3%、3.0%、15.9%;烟叶和甘蔗种植面积分别减少8.7%和1.1%;蔬菜、瓜果、油料、甘蔗等产量均有不同程度的增长。
B.

【单选题】文字资料一 根据国家统计局对全国19500家各种类型企业的调查显示:一季度,全国企业家信心指数为142.0,创下近年最高水平,并首次攀至140.0以上的景气高位。有48.4%的企业家对所在行业总体运行状况持乐观的态度,45.1%的企业家认为变化不大,______,具体表现在:各行业企业家对宏观经济发展信心继续增强。一季度,制造业、建筑业、交通运输仓储和邮政业、...
A.
133.1 124.8
B.
128.2 133.1
C.
128.2 124.8
D.
124.8 128.2
【单选题】Questions 21 and 22 are based on the following news. At the end of the news item, you will be given 10 seconds to answer the questions. Now, listen to the news. How many members are there in the...
A.
13.
B.
23.
C.
22.
D.
15.
【单选题】Many theories concerning the causes of juvenile delinquency (crimes committed by young people) focus either on the individual or on society as the major contributing influence. Theories (31) on the i...
A.
considering
B.
ignoring
C.
highlighting
D.
discarding
【单选题】2007年5月7日,上海市浦东新区税务稽查大队某队稽查员褚某根据单位安排对群众举报反映上海和力建材有限公司(以下简称和力公司)逃避缴纳税款的问题进行突击稽查,查获内销进口建材不入账共计35.6万元的四本自制收据。同月26日,浦东新区税务案件侦查室又将该室收到的和力公司逃避缴纳税款的举报材料移送至稽查大队。褚某在查阅该举报材料时,发现和力公司经理刘某在中国银行浦东分行的存放账外销售款的存折及有关单据...
A.
徇私舞弊不征、少征税款罪
B.
玩忽职守罪
C.
徇私枉法罪
D.
滥用职权罪
【单选题】2004年,粮食作物的总植面积与总产量比2003年减少的百分比约为()。 A.5.8%与6.6% B.1.8%与11.95% C.60.2%与15.9% D.1.8%与6.6%
A.
2004年某省种植业结构继续调整,粮食作物的种植面积占农作物种植总面积比例由上午的60.2%调整为58.4%,年粮食作物种植面积147.11万公顷,比去年减少9.0公顷,粮食总产量713.16万公顷,其中春、夏、秋粮所占比例如下图所示。与去年相比,春粮减产5.31万吨,夏粮减产2.37万吨,秋粮减产42.38万吨,总产量下降50.06万吨。非粮食作物中的油料、蔬菜、药材种植面积分别增长1.3%、3.0%、15.9%;烟叶和甘蔗种植面积分别减少8.7%和1.1%;蔬菜、瓜果、油料、甘蔗等产量均有不同程度的增长。
B.

【单选题】将以下6个句子重新排列组合,正确的顺序应为( )。 ①构建和谐社会,既要实现代内公平,又要实现代际公平,并正确处理好代内公平与代际公平的关系。 ②因此,代际公平最鲜明地体现了和谐社会的两个重要特征,即“公平正义”和“人与自然和谐相处”。 ③这两个重要特征都反映在“既满足当代人的需要,又不对后代人满足其需要的能力构成危害的发展”这一可持续发展观的深刻内涵之中。 ④随着资源、环境和生态等现代性问题的日...
A.
②⑤①③④⑥
B.
④⑥②③⑤①
C.
④⑥②③①⑤
D.
⑤③④②①⑥

相关题目:
【单选题】2003年非粮食作物的种植总面积约为()。 A.62万公顷 B.156万公顷 C.138万公顷 D.103万公顷
A.
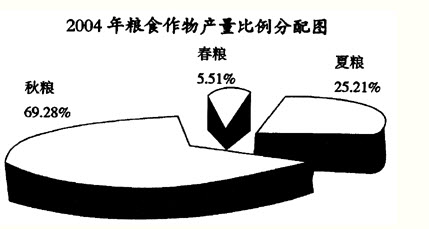
2004年某省种植业结构继续调整,粮食作物的种植面积占农作物种植总面积比例由上午的60.2%调整为58.4%,年粮食作物种植面积147.11万公顷,比去年减少9.0公顷,粮食总产量713.16万公顷,其中春、夏、秋粮所占比例如下图所示。与去年相比,春粮减产5.31万吨,夏粮减产2.37万吨,秋粮减产42.38万吨,总产量下降50.06万吨。非粮食作物中的油料、蔬菜、药材种植面积分别增长1.3%、3.0%、15.9%;烟叶和甘蔗种植面积分别减少8.7%和1.1%;蔬菜、瓜果、油料、甘蔗等产量均有不同程度的增长。
B.


【单选题】文字资料一 根据国家统计局对全国19500家各种类型企业的调查显示:一季度,全国企业家信心指数为142.0,创下近年最高水平,并首次攀至140.0以上的景气高位。有48.4%的企业家对所在行业总体运行状况持乐观的态度,45.1%的企业家认为变化不大,______,具体表现在:各行业企业家对宏观经济发展信心继续增强。一季度,制造业、建筑业、交通运输仓储和邮政业、...
A.
133.1 124.8
B.
128.2 133.1
C.
128.2 124.8
D.
124.8 128.2
【单选题】Questions 21 and 22 are based on the following news. At the end of the news item, you will be given 10 seconds to answer the questions. Now, listen to the news. How many members are there in the...
A.
13.
B.
23.
C.
22.
D.
15.
【单选题】Many theories concerning the causes of juvenile delinquency (crimes committed by young people) focus either on the individual or on society as the major contributing influence. Theories (31) on the i...
A.
considering
B.
ignoring
C.
highlighting
D.
discarding
【单选题】2007年5月7日,上海市浦东新区税务稽查大队某队稽查员褚某根据单位安排对群众举报反映上海和力建材有限公司(以下简称和力公司)逃避缴纳税款的问题进行突击稽查,查获内销进口建材不入账共计35.6万元的四本自制收据。同月26日,浦东新区税务案件侦查室又将该室收到的和力公司逃避缴纳税款的举报材料移送至稽查大队。褚某在查阅该举报材料时,发现和力公司经理刘某在中国银行浦东分行的存放账外销售款的存折及有关单据...
A.
徇私舞弊不征、少征税款罪
B.
玩忽职守罪
C.
徇私枉法罪
D.
滥用职权罪
【单选题】2004年,粮食作物的总植面积与总产量比2003年减少的百分比约为()。 A.5.8%与6.6% B.1.8%与11.95% C.60.2%与15.9% D.1.8%与6.6%
A.
2004年某省种植业结构继续调整,粮食作物的种植面积占农作物种植总面积比例由上午的60.2%调整为58.4%,年粮食作物种植面积147.11万公顷,比去年减少9.0公顷,粮食总产量713.16万公顷,其中春、夏、秋粮所占比例如下图所示。与去年相比,春粮减产5.31万吨,夏粮减产2.37万吨,秋粮减产42.38万吨,总产量下降50.06万吨。非粮食作物中的油料、蔬菜、药材种植面积分别增长1.3%、3.0%、15.9%;烟叶和甘蔗种植面积分别减少8.7%和1.1%;蔬菜、瓜果、油料、甘蔗等产量均有不同程度的增长。
B.


【单选题】将以下6个句子重新排列组合,正确的顺序应为( )。 ①构建和谐社会,既要实现代内公平,又要实现代际公平,并正确处理好代内公平与代际公平的关系。 ②因此,代际公平最鲜明地体现了和谐社会的两个重要特征,即“公平正义”和“人与自然和谐相处”。 ③这两个重要特征都反映在“既满足当代人的需要,又不对后代人满足其需要的能力构成危害的发展”这一可持续发展观的深刻内涵之中。 ④随着资源、环境和生态等现代性问题的日...
A.
②⑤①③④⑥
B.
④⑥②③⑤①
C.
④⑥②③①⑤
D.
⑤③④②①⑥

参考解析:


AI解析
重新生成

题目纠错 0
发布

 复制链接
复制链接 新浪微博
新浪微博 分享QQ
分享QQ 微信扫一扫
微信扫一扫





